An analysis of technological drivers in IT infrastructure.
1. Introduction:
The evolution of information technologies had mixed impacts on the business world, which helped increase opportunities for organisations and helped them gain more customers with good potential (Winston, 2012). One of the biggest benefits of the information technology was in the management of the information inside and outside the organisation. In short, newly evolved information technologies created a good MIS system and increased the strength of relationships between the customers and organisations (James, 2013). This assignment has the purpose of discussing the IT infrastructure and identifies the main technological drivers in the evolution of IT infrastructure. From the discussion, a critical analysis of these technological drivers will be made to discuss the most influential technology.
2. IT (Information Technology) Infrastructure:
The concept of information technology infrastructure has been used over a long period of time and a general or a widely defined definition is not available in any of the literatures (Laan, 2011). In the simplest context, IT infrastructure can be defined as the framework, which is integrated, over which the digital networks will be operating. It can consist of software, systems, equipments and services that are used by the organisation (Gupta, 2010). Another definition of the term defines an IT infrastructure as the framework of different components with the aim of providing the customers with IT services and information management (Pour, 2006). It is a combination of different hardware and software through which operations in the enterprise is handled.
Figure 1: IT Infrastructure according to different perspectives
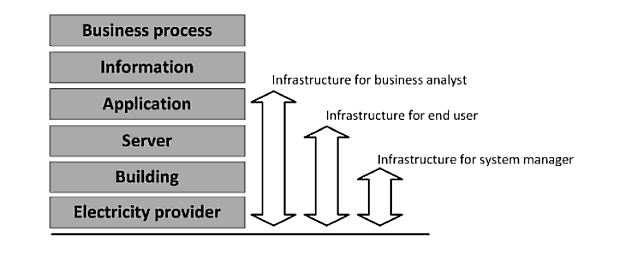
Source: Laan, 2011
The visibility of the IT infrastructure needs to be observed based on the perceptions of the people who access the IT infrastructure. In the perception of a user, the main visible components of the infrastructure are the applications, services and the systems that give access to both these elements. The physical implementation of the system will be invisible. For a systems manager, the main visible elements will be the servers, building and resources within building. The application will be invisible to these people. For the case of a business analyst, the method of management of the information is the prime element and must be viewed with this perspective (Laan, 2011). Figure 1 gives an explanation of the information discussed above.
The evolution of the IT infrastructure began with the introduction of mainframe computers in 1958 by IBM. In this, the information management was through the mainframe computer, which is large in size. Later in 1981 personal computers began to emerge where a peer to peer transfer of information was established. At present, a client server infrastructure is established where the client is always connected to the server over the internet and the services are designed based on the requirements of the client (Rainer, Cegielski, 2010).
3. Technological Drivers that Supported the IT Infrastructure Evolution:
During the process of evolution, many researches were carried out and new innovated technologies were found one after the other. On analysing the emergence of new technologies, it can be seen that as a new technology was found, customers increased their expectation level that demanded further evolution of a more enhanced technology (Shane, 2008). A simple example can be taken from the mobile communication world. Initially, the need of the customers was to send voice messages over the line. As telegraph was introduced, the concept of voice messages changed to digital transmission. Accordingly second generation communication technologies were found. Later this was changed by the third generation technologies as a result of the changing demand of the customers to transfer voice and video messages simultaneously (Arokiamary, 2009). At present, the research is on the evolution of fourth generation technologies that uses heterogeneous networks in communication and the customer will be able to communicate without interruption and can transfer the data at the highest speed possible (Mapp, et.al, 2010). Accordingly, as new technologies were introduced the demands of the customers were also changing to the next level. Some of the main technological drivers that supported the evolution of IT infrastructure are explained below,
Evolution of microprocessor:
The microprocessor originated in the early 1960’s and was a breaking revolution in the design of computer hardware. An observation was made by Gordon Moore in the year 1965 which quoted that use of microprocessors in hardware components will increase to double every two years of time (Null, Lobur, 2010). This year was later changed to 18 months and observed the following as,
- The microprocessor power will double in eighteen months of time
- In the same period, the computing power will also increase to double
- The price will be reduced to half in the same time-frame (Brock, Moore, 2006)
According to the Moore’s Law, the performance will be increase in fixed time intervals and the number of transistors or microprocessors that make up the hardware also increases. The main significance of the nanotechnology was the reduction of the cost. The incorporation of more transistors in the limited space available reduced the cost of hardware and it became possible for most customers to purchase the hardware. For example, when one of the mainframe computers was introduced by IBM initially, the price of such computers was outside the scope of a customer (Dreamtech, 2006). If we evaluate the present situation, the size of the computers has decreased dramatically and the customers can purchase high speed computers at lower prices with far more configuration compared to the old mainframe computers.
Relevance of emergence of law of mass-digital storage:
Figure 2: Price change in the storage devices over the years
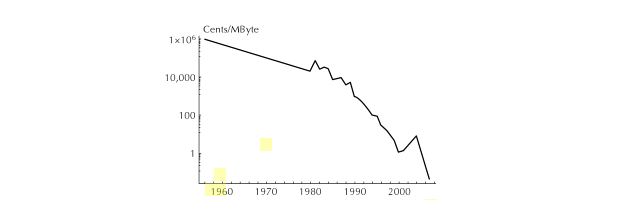
Source:Cooper, et.al, 2009
According to the law of mass-digital storage, there is an increase in the data produced in each year and the increase of data can be observed to be doubling each year. As the amount of data increases, the cost for storing the information reduced considerably. The best example for this can be analysed as follows. In the 1960’s the cost of one cent per megabyte of data was one million and in the 2000, the cost of one terabyte of storage went down to 340 US Dollars (Cooper, et.al, 2009). The need for one terabyte of storage was least needed in 1960’s but at present, the requirement of more storage is very important. The changes in the price of the storage space are given in figure 2. The use of Nanotubes was one of the tubes that helped in the achievement of such high data storage and the reduction of the cost of the storage space (Laudon & Laudon, 2006).
Evolution of Ethernet:
The evolution of the Internet was another main revolution in the communication world. Robert Metcalfe was the key person behind the invention of the Ethernet technology. According to the researches, the importance of the network and use of the network increases as more people join the network (Spurgeon, 2009). As more and more users are connected to the network, the communication cost over the Internet also reduces considerably. According to the estimates known at present, millions of people have access to the Internet and Iinternet communication gained more market desire over the telephonic communication or the exchange of the information through the wired networks. At present, the communication is more focused on wireless communications (Verma, 2011). With the evolution of Internet communication, more network standards begin to emerge and the World Wide Web arose to become a major component of communication.
Fourth Generation:
Presently, research is being carried out to evolve fourth generation network standards, where the users communicate with each other without interruption in the communication. The new concept of fourth generation argues that even if one of the networks fails, the system can check for other networks that are available. Through this available network, the user communicates with the other party without any interruption. Here the operations will be controlled by the heterogeneous networks (Sesia, et.al, 2011).
4. The most influential technological component:
The evolution of IT infrastructure was a revolution that brought forward many benefits to the public. Both organisations and the public took advantage of the emergence of new technologies. For a simple example, customers used to have to go into their banks to carry out all transactions. The situation is different now as all banking organisations have internet banking facilities where the users can manage their funds at home. The organisations have the benefit of managing their information in an efficient method, while users get the advantage of saving time and hassle in accessing the services. In total, the evolution of the IT infrastructure redefined the way information has been managed within the organisation and outside of the organisation.
In previous sections the author discussed the different technological drivers that supported the development of today’s efficient IT infrastructure. Each of the technological drivers has an importance of their own and supported the development of the next higher revolution. According to the analysis by the author, the most influential among the technological drivers was the discovery of microprocessors and the concept of Moore’s Law. The development of the IT infrastructure started with this and through the microprocessor and nanotechnology, the developers were able to incorporate many transistors under one circuit board.
Maslow, one of the greatest researchers of human motivation, states that there are certain levels of motivation with regards to a person. The need for motivation starts from the lowest level and once the needs in a particular level are fulfilled, the search for the needs in the next level will begin (Zastrow, Ashman, 2010). The same theory can be applied here. As it became a reality that more microprocessors could be incorporated in a single board, the next demand was put forward in agenda where they need to increase the storage space. This was followed by the need for high transfer of data between the communicating users. Finally the Internet technology evolved and everything at present is controlled by the World Wide Web. If the customer needs to collect any information, book some service or whatever the demand is, they can use the Internet to find a solution. Similarly the organisation could also provide their services and manage information through the use of Internet. There are benefits for the organisation in terms of efficiently managing the data within the organisation. For example, if there is problem with the computers in one of the offices, through the use of remote logging the systems administrator can manage and control the faulty system from a distance. Actually the evolution of the IT infrastructure gave many opportunities and choices for an organisation. Whatever organisations and customers enjoy at the moment started with the finding of the microprocessor and therefore this technological driver can be considered the most influential technological driver.
5. Conclusion:
The above paper analysed the evolution of the IT infrastructure and the technological drivers that supported the evolution. It started with microprocessors and is currently under the research for evolution of fourth generation network technologies. All these technological innovations produced benefits to the business world where the customers and the organisations were the recipients of the benefits. The needs of the human beings are not fixed and it changes, which accordingly results in the evolution of more and more new innovative technologies in the future.
References:
Arokiamary, J., (2009). Mobile Communications, Technical Publications, pp. 100 – 105
Brock, D., Moore, G.E., (2006). Understanding Moore’s Law: Four Decades of Innovation, Chemical Heritage Foundation,
Cooper, C., Goswami, U., Sahakian, B., (2009). Mental Capital and Wellbeing, John Wiley & Sons,
Dreamtech, (2006). Ibm Mainframe Black Book New Edition, Dreamtech Press, pp. 189 – 196
Gupta, G., (2010). It Infrastructure & Its Management, Tata McGraw-Hill Education,
James, J., (2013). Information Technology and Development: A New Paradigm for Delivering the Internet to Rural Areas in Developing Countries, Routledge,
Laan, S., (2011). It Infrastructure Architecture: Infrastructure Building Blocks and Concepts, Sjaak Laan Publishers
Laudon, K.C., Laudon, J.P., (2006). Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm, Pearson/Prentice Hall, 9th Edition
Null, L., Lobur, J., (2010). The Essentials of Computer Organization and Architecture, Jones & Bartlett Publishers, 3rd Edition
Pour, M., (2006). Emerging Trends and Challenges in Information Technology Management: 2006 Information Resources Management Association International Conference, Idea Group Inc
Rainer, R.K., Cegielski, C., (2010). Introduction to Information Systems: Enabling and Transforming Business, John Wiley & Sons, 3rd Edition
Sessia, S., Toufik, I., Baker, M., (2011). LTE – The UMTS Long Term Evolution: From Theory to Practice, John Wiley & Sons, 2nd Edition
Shane, S., (2008). The Handbook of Technology and Innovation Management, John Wiley & Sons,
Spurgeon, C., (2009). Ethernet: The Definitive Guide, O’Reilly Media, pp. 111 – 118
Verma, A., (2011). Dependability of Networked Computer-based Systems, Springer Publications, Pages: 105 – 116
Winston, B., (2012). Media Technology and Society, Routledge Publications, 3rd Editiuon
Zastrow, C., Ashman, K., (2010). Understanding Human Behavior and the Social Environment, Cengage Learning, 8th Edition, Pages: 440 – 450