Neisseria meningitidis
Abstract
Neisseria meningitidis causes meningitis and/or septicaemia in children and young adults resulting in considerable morbidity and mortality. Searching of NCBI databases with the term “Factor H binding protein, Neisseria meningitidis” identified two proteins important in N. meningitidis biology: Neisseria surface protein A (nspA) and the porin B (porB). Predicted protein domains of Factor H binding protein, nspA and porB were retrieved following blastp searches. In contrast, searching of NCBI databases with “lnt and Neisseria meningitidis MC58” retrieved no additional proteins although predicted protein domains of lnt were retrieved.
Introduction
Neisseria meningitidis is a pathogenic species of bacteria which causes meningitis and/or septicaemia in children and young adults. It is responsible for both sporadic cases of meningitis and epidemics of the disease worldwide, producing considerable morbidity and mortality (Rouphael and Stephens, 2012). N. meningitides is a -proteobacteria with the taxonomic lineage of: Bacteria; Proteobacteria; Betaproteobacteria; Neisseriales; Neisseriaceae; Neisseria (NCBI Taxonomy Browser, 2015). The majority of N. meningitidis strains which cause disease are classified as serogroup A, B or C, with the expression of specific capsular polysaccharides determining the serogroup type (Rouphael and Stephens, 2012; Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, 2015). Strains of N. meningitides which cause epidemics in developing countries are generally typed as serogroup A, whereas serogroup B and C strains cause meningitis outbreaks in the developed world (Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, 2015). Immunological immunoreactivity of N. meningitidis strains has identified a further three serogroups (W-135, X and Y) in addition to serogroups A, B and C which cause life threatening disease (Rouphael and Stephens, 2012). A quadrivalent meningococcal conjugate vaccine against serogroups A, C, Y and W-135 has been developed which is recommended in the USA for young children (Rouphael and Stephens, 2012).
The complete nucleotide sequence of a number of N. meningitis strains have been determined with the serogroup A strain Z2491 (Parkhill et al., 2000) and the serogroup B strain MC58 (Tettelin et al., 2000) being the first to be completely sequenced. Sequencing of N. meningitis strain Z2491 determined that the genome was 2,184,406 base pairs in length, with a predicted 2,121 coding sequences; and the genome of the serogroup B strain MC58 was sized 2,272,351 base pairs with a predicted 2,158 coding sequences (Parkhill et al., 2000; Tettelin et al., 2000). Of the 2,158 predicted coding sequences in strain MC58, just over half of them (1,158, 53.7%) were assigned a biological function (Tettelin et al., 2000). The genome sequence of several other N. meningitides strains have been determined (Rouphael and Stephens, 2012) including the serogroup B strain H44/76 (Piet et al., 2011) and show that the N. meningitides genome is about 2.0 – 2.2 megabases in length, containing around 2,000 genes (Rouphael and Stephens, 2012).
In common with other Gram negative bacteria, the gross structure of the subcapsular cell envelope of N. meningitidis comprises an outer membrane, a peptidoglycan layer between the two cell membranes known as the periplasmic space, and an inner or cytoplasmic membrane (Rouphael and Stephens, 2012).
Two serogroup B vaccines which have recently been developed against N. meningitidis contain factor H binding protein (Giuntini et al., 2015). Searches of NCBI databases using this term were conducted in order to determine information regarding the biology of this protein. A second search was done using lnt apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase which acrylates membrane lipoproteins.
Methods
The initial search of all NCBI databases (url: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gquery/) was with the term “Factor H binding protein, Neisseria meningitidis”. This identified two genes which were explored further.
A search of the NCBI Protein database (url: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/) retrieved the protein accession number which was used to identify proteins with related amino acid sequences using blastp (Altschul et al., 1997) from the NCBI BLAST website (url: http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?CMD=Web&PAGE_TYPE=BlastHome). Blastp also provided information on conserved domain database (CDD) analysis of the query protein sequence (Marchler-Bauer et al. 2015).
Results
A search of all NCBI databases with “Factor H binding protein, Neisseria meningitidis” retrieved a number of entries including two from NCBI Gene with a match to N. meningitidis genes: nspA outer membrane protein [ Neisseria meningitidis MC58 ] (NCBI Gene, 2015a); and porB major outer membrane protein PIB [ Neisseria meningitidis MC58 ] (NCBI Gene, 2015b).
Neisserial surface protein A (nspA)
A search of the NCBI Protein database with Nspa retrieved its accession number, NP_273705 and showed that the protein comprised 174 amino acids (NCBI Protein, 2015a). Following a blastp search of non-redundant (nr) protein sequences several conserved domains were identified on Nspa (Figure 1). This included a specific hit with the Opacity (accession number pfam02462) family porin protein domain which mediate a range of interactions between the pathogen and host cells (NCBI Conserved Protein Domain Family, 2015a). Non specific hits against the LomR domain – Opacity protein and related surface antigens, and the gram_neg_porins domain (see porB below) were also identified.
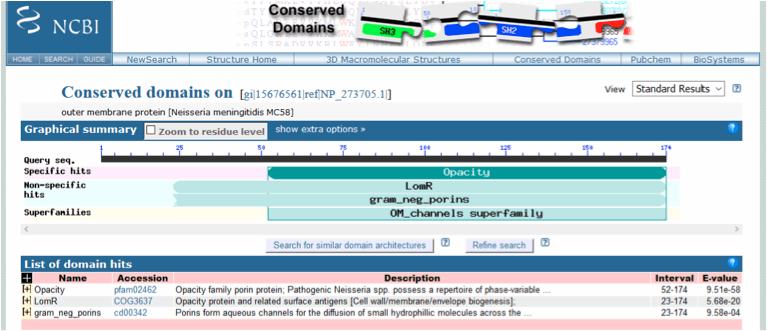
Figure 1. Conserved domain database (CDD) analysis of Neisserial Surface Protein a (Nspa) following a blastp search of nr protein sequences with the accession number NP_273705.
Retrieved blastp protein matches of Nspa (accession number NP_273705) included high degrees of identity with proteins from N. meningitidis and other Neisseria species. These included 100% identity with outer membrane protein [Neisseria meningitidis], accession number WP_002225511.1; 99% identity with membrane protein [Neisseria meningitidis], accession number WP_002217717.1; and 97% identity with membrane protein [Neisseria lactamica], accession number WP_019272820.1. The match with the membrane protein from N. lactamica is shown in Figure 2.
membrane protein [Neisseria lactamica]
Sequence ID: ref|WP_019272820.1|Length: 174, Number of Matches: 1
Alignment statistics for match #1
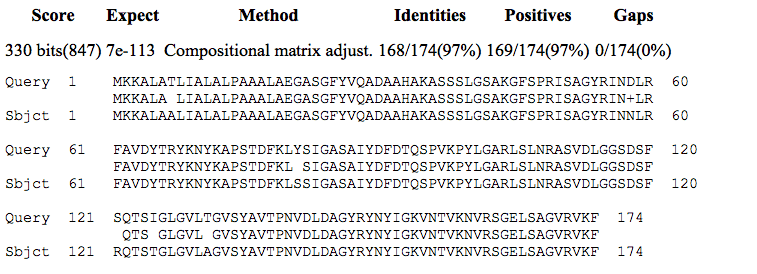
Figure 2. Alignment of the Neisserial Surface Protein a (Nspa) from N. meningitidis (NP_273705, Query) with the membrane protein from N. lactamica (WP_019272820.1, Subject).
The NCBI Gene file on nspA outer membrane protein identified several relevant references on the structure and function of the protein (NCBI Gene, 2015a). This included one on the crystal structure of the protein which was determined to a resolution of 2.55 Angstroms (Vandeputte-Rutten al., 2003) and is shown in Figure 3. nspA interacts with ethanolamine, sulphate ions and n-octyltetraoxyethylene (NCBI Structure, 2012).
Figure 3. Molecular graphic of the crystal structure of Neisserial Surface Protein a (nspA). From: NCBI Structure (2012).
porB major outer membrane protein PIB
Interrogation of the NCBI Protein database with Porb identified a protein comprising 331 amino acids termed “major outer membrane protein PIB [Neisseria meningitidis MC58]”, with an accession number NP_275030.1 (NCBI Protein, 2015b). A blastp search using NP_275030.1 identified the gram_neg_porins (accession number cd00342) domain within the protein. This is shown in Figure 4. The pore structure of porins is formed by the formation of trimeric proteins which enables the diffusion of small hydrophillic molecules including glucose (NCBI Conserved Protein Domain Family, 2015b).
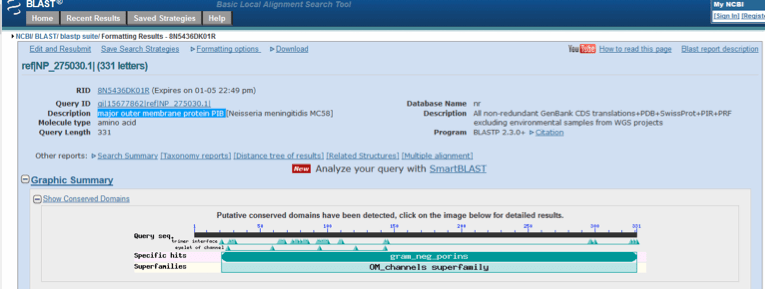
Figure 4. Conserved domain database (CDD) analysis of major outer membrane protein PIB following a blastp search of nr protein sequences with the accession number NP_275030.1.
blastp matches with NP_275030.1 retrieved multiple significant hits such as 100% identity with porin {class 3 serotype 15} [Neisseria meningitidis, MC58, Peptide, 312 aa], accession number AAB24224.1; 100% identity with PorB [Neisseria meningitidis] accession number AAA03392.1; and 97F% identity with class 3 outer membrane protein [Neisseria meningitidis] accession number AAU93401.1 (Figure 5).
class 3 outer membrane protein [Neisseria meningitidis]
Sequence ID: gb|AAU93401.1|Length: 317, Number of Matches: 1
Alignment statistics for match #1
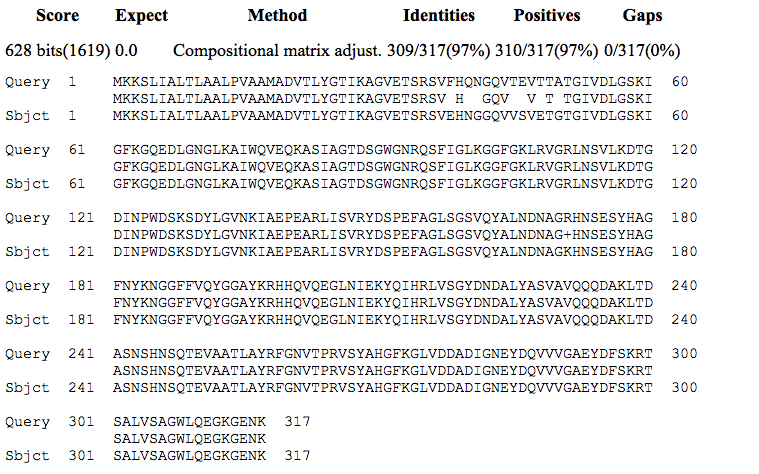
Figure 5. Alignment porB major outer membrane protein PIB from N. meningitidis (NP_275030.1, Query) and class 3 outer membrane protein from N. meningitidis (AAU93401.1, Subject).
Factor H binding protein
A search of the NCBI Protein database with “factor H binding protein, Neisseria meningitides” retrieved the entry for this protein with a Genbank accession number of AEX92830.1. This showed that factor H binding protein from N. meningitidis was comprised of 276 amino acids (NCBI Protein, 2015b). Conserved domain database (CDD) analysis showed that the protein had a conserved Lipoprot_C domain and was thus a member of the lipoprotein C superfamily (Figure 6). Lipoprot_C (accession number pfam08794) is formally described as “Lipoprotein GNA1870 C terminal like” which is a Meningococcal antigen which is exposed on the bacterial surface of N. meningitidis (NCBI Conserved Protein Domain Family, 2015c).
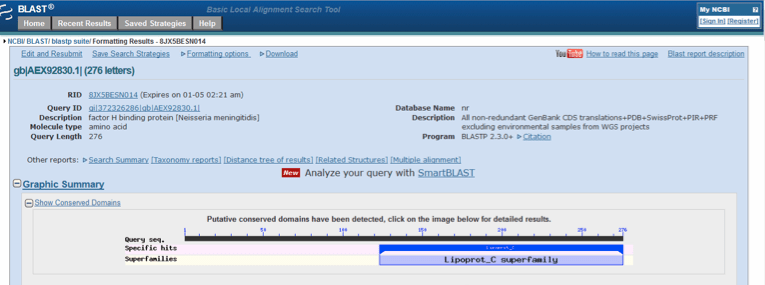
Figure 6. Conserved domain database (CDD) analysis of factor H binding protein [Neisseria meningitidis] following a blastp search of nr protein sequences with the accession number AEX92830.
Retrieved blastp protein matches of AEX92830.1 with highly significant alignments were N. meningitidis proteins including chorismate binding enzyme [Neisseria meningitidis], accession number WP_002241944.1 with 100% identity; and a series of entries for factor H-binding protein [Neisseria meningitidis] with high matches such as accession number ADB89963.1 which had 98% identity with AEX92830.1. Overall, the top 100 protein sequence hits with a high degree of identity to the query sequence (accession number ADB89963.1) were described as N. meningitidis “factor H-binding protein” or “lipoprotein”. The range of identity to the target sequence was 89% to 100%. One example of a match with ADB89963.1 is shown in Figure 7 with a 95% amino acid identity being recorded between the Query and Subject sequences. blastp searches of reference protein (refseq_protein) sequences with AEX92830.1 produced similar results.
lipoprotein [Neisseria meningitidis]
Sequence ID: ref|WP_002251539.1|Length: 279, Number of Matches: 1
Alignment statistics for match #1

Figure 7. Alignment of factor H-binding protein sequence from N. meningitidis (AEX92830.1, Query) with N. meningitidis (WP_002251539.1, Subject).
lnt apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase
A second search of all NCBI databases with “lnt and Neisseria meningitidis MC58” retrieved a single entry from NCBI Gene: lnt apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase [ Neisseria meningitidis MC58 ] (NCBI Gene, 2015c). Information within this file showed that the protein (accession number NP_273755.1) functioned in the transfer of a fatty acyl group on membrane lipoproteins. Accessing the NCBI Protein database with the accession number NP_273755.1, identified apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase which consisted of 524 amino acids (NCBI Protein, 2015c). A blastp search of nr sequences with the accession number NP_273755.1 identified several conserved domains within the lnt protein (Figure 8), with both specific and non-specific hits being recorded. The specific hit was with the ALP_N-acyl_transferase (accession number cd07571) domain. ALP_N-acyl_transferase is Apolipoprotein N-acyl transferase, a class 9 nitrilase, which has an essential function in gram-negative bacteria as a membrane bound enzyme, catalysing the N-acylation of apolipoproteins in the final stage of lipoprotein maturation (NCBI Conserved Protein Domain Family, 2015d). The analysis of conserved domains identified lnt protein as being a member of the nitrilase superfamily.
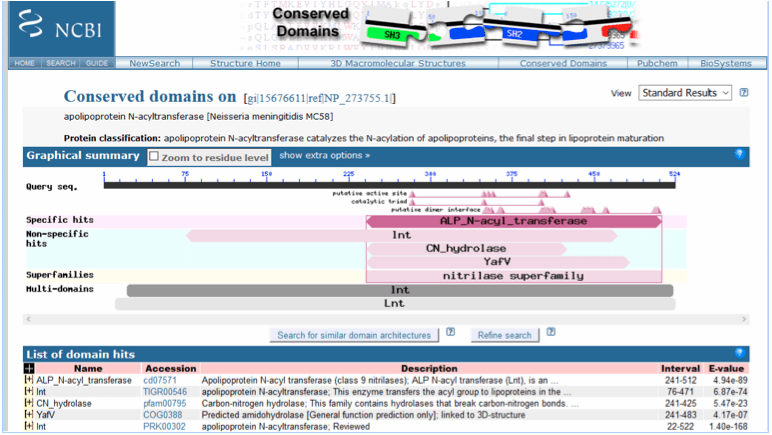
Figure 8. Conserved domain database (CDD) analysis of lnt apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase [Neisseria meningitidis MC58] following a blastp search of nr protein sequences with the accession number NP_273755.1.
Analysis of protein matches with NP_273755.1 following blastp searches identified a series of apolipoprotein N-acyltransferases from N. meningitidis strains with very high amino acid identity such as apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase [Neisseria meningitidis] (accession number WP_002225467.1) which had 100% identity. High matches were also found with apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase from other Neisseria species following a blastp search of NCBI Protein Reference Sequences. These included Neisseria polysaccharea with a 97% identity overall (accession number WP_003753191.1); Neisseria gonorrhoeae with 96% identity (accession number WP_047926209.1); and Neisseria lactamica with 92% identity (accession number WP_013449282.1). The alignment of protein sequences of apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase [Neisseria meningitidis] (NP_273755.1) with apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase from Neisseria polysaccharea (WP_003753191.1) is shown in Figure 9.
Sequence ID: ref|WP_003753191.1|Length: 512, Number of Matches: 1
Range 1: 1 to 512
Alignment statistics for match #1
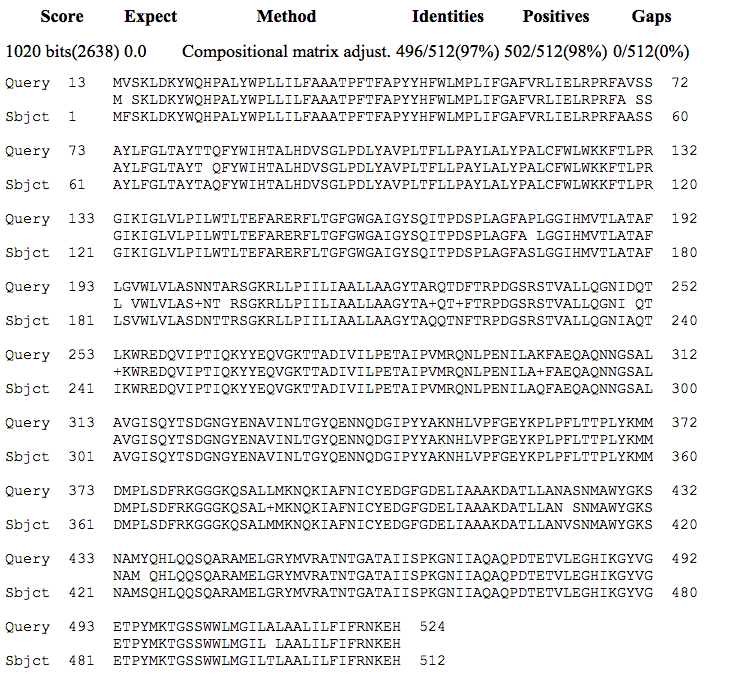
Figure 9. Alignment of apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase protein sequences from N. meningitidis (NP_273755.1, Query) and N. polysaccharea (WP_003753191.1, Subject).
Discussion
Bioinformatic searches using Factor H binding protein as the query term identified two important N. meningitidis proteins: Neisserial surface protein A (nspA) and the porin, porB. nspA has been identified as a conserved outer membrane protein on the N. meningitides bacterium with the potential for vaccine development (Vandeputte-Rutten al., 2003). Blastp matches using one query nspA sequence identified matches with nspA proteins from other species of Neisseria, as well as N. meningitidis, which confirms that nspA is conserved in the genus.
porB is one of two porin proteins expressed in N. meningitidis (the other is PorA). Both have a function in allowing diffusion of small hydrophilic nutrients into the bacterium due to selection of cations and anions. PorB is the major outer membrane porin which inserts into eukaryotic membranes (Rouphael and Stephens, 2012). The protein induces calcium ion influx into immune cell targets – the antigen-presenting cells, and activates Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) causing cell apoptosis (Massari et al., 2003). The related protein, PorA is a major component of vaccines against N. meningitidis serotype B which are based on outer membrane vesicles (Rouphael and Stephens, 2012).
Recently, both nspA and porB3 were shown to enhance resistance of N. meningitidis to complement-mediated bactericidal activity which is usually dependent on factor H binding protein (Giuntini et al., 2015).
High blastp matches of lnt apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase from N. meningitidis with lnt from other Neisseria species indicates that the protein is highly conserved in the Neisseria genus. In contrast to searches with factor H binding protein no other proteins were identified by bioinformatics searches with lnt. This illustrates a limitation of bioinformatics searching for predicting biological processes.
In conclusion, bioinformatics should be applied in conjunction with experimental data e.g. experiments to investigate the attachment and invasion of N. meningitidis to host cells which were recently described by Bartley et al. (2013) to enable a full understanding of biological processes, such as the biology and pathogenicity of N. meningitidis.
References
Altschul, S.F., Madden, T.L., Schäffer, A.A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W. & Lipman, D.J. (1997). Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Research. 25, 3389-3402.
Bartley SN., Tzeng Y.L., Heel K., Lee C.W., Mowlaboccus S., Seemann T., Lu W., Lin Y.H., Ryan C.S., Peacock C., Stephens D.S., Davies J.K. & Kahler C.M. (2013). Attachment and invasion of Neisseria meningitidis to host cells is related to surface hydrophobicity, bacterial cell size and capsule. PLoS One. 8(2), e55798.
Giuntini S., Pajon R., Ram S. & Granoff D.M. (2015). Binding of complement factor H to PorB3 and NspA enhances resistance of Neisseria meningitidis to anti-factor H binding protein bactericidal activity. Infection and Immunity.83(4), 1536-1545.
Marchler-Bauer A., Derbyshire M.K., Gonzales NR., Lu S., Chitsaz F., Geer LY., Geer R.C., He J., Gwadz M., Hurwitz D.I., Lanczycki C.J., Lu F., Marchler G.H., Song J.S., Thanki N., Wang Z., Yamashita R.A., Zhang D., Zheng C. & Bryant S.H. (2015), CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Research.43(D), 222-226.
Massari P., Ram S., Macleod H, & Wetzler L.M. (2003). The role of porins in neisserial pathogenesis and immunity. Trends in Microbiology. 11, 87-93.
NCBI Conserved Protein Domain Family (2015a). Opacity. Retrieved 4th January 2015 from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi?ascbin=8&maxaln=10&seltype=2&uid=pfam02462
NCBI Conserved Protein Domain Family (2015b). Retrieved 4th January 2015 from:
NCBI Conserved Protein Domain Family (2015c). Lipoprot_C. Retrieved 4th January 2015 from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi?ascbin=8&maxaln=10&seltype=2&uid=pfam08794
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cddsrv.cgi?ascbin=8&maxaln=10&seltype=2&uid=cd07571
NCBI Gene (2015a). nspA outer membrane protein [ Neisseria meningitidis MC58 ]. Retrieved 4th January 2016 from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/902774
NCBI Gene (2015b). porB major outer membrane protein PIB [ Neisseria meningitidis MC58 ].Retrieved 4th January 2016 from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/904054
NCBI Gene (2015c). lnt apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase [ Neisseria meningitidis MC58 ]. Retrieved 4th January from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/?term=lnt,%20Neisseria%20meningitidis
NCBI Protein (2015a). outer membrane protein [Neisseria meningitidis MC58]. Retrieved 4th January 2015 from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/15676561
NCBI Protein (2015b). major outer membrane protein PIB [Neisseria meningitidis MC58]. Retrieved 4th January 2015 from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/15677862
NCBI Protein (2015c). factor H binding protein [Neisseria meningitidis]. Retrieved 4th January 2015 from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/AEX92830.1
NCBI Protein (2015d). apolipoprotein N-acyltransferase [Neisseria meningitidis MC58]. Retrieved 4th January 2015 from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/15676611
NCBI Structure (2012). Crystal Structure of Neisserial Surface Protein a (Nspa). Retrieved 4th January 2016 from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/mmdb/mmdbsrv.cgi?uid=24329
NCBI Taxonomy Browser (2015). Neisseria meningitides. Retrieved 31st January 2015 from:: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=487&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock
Parkhill J., Achtman M., James K.D., Bentley S.D., Churcher C., Klee S.R., Morelli G., Basham D., Brown D., Chillingworth T., Davies RM., Davis P., Devlin K., Feltwell T., Hamlin N., Holroyd S., Jagels K., Leather S., Moule S., Mungall K., Quail M.A., Rajandream M.A., Rutherford K.M., Simmonds M., Skelton J., Whitehead S., Spratt B.G & Barrell B.G. (2000). Complete DNA sequence of a serogroup A strain of Neisseria meningitidis Z2491. Nature. 404(6777), 502-506.
Piet J.R., Huis in ‘t Veld R.A., van Schaik B.D., van Kampen A.H., Baas F., van de Beek D., Pannekoek Y. & van der Ende A. (2011). Genome sequence of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B strain H44/76. Journal of Bacteriology. 193(9), 2371-2372.
Rouphael N.G. & Stephens D.S. (2012). Neisseria meningitides: Biology, Microbiology, and Epidemiology. Methods in Molecular Biology. 799, 1-20.
Tettelin, H., Saunders, N.J., Heidelberg, J., Jeffries, A.C., Nelson, K.E., Eisen, J.A., Ketchum, K.A., Hood, D.W., Peden, J.F., Dodson, R.J., Nelson, W.C., Gwinn, M.L., DeBoy, R., Peterson, J.D., Hickey, E.K., Haft, D.H., Salzberg, S.L., White, O., Fleischmann, R.D., Dougherty, B.A., Mason, T., Ciecko, A., Parksey, D.S., Blair, E., Cittone, H., Clark, E.B., Cotton, M.D., Utterback, T.R., Khouri, H., Qin, H., Vamathevan, J., Gill, J., Scarlato, V., Masignani, V., Pizza, M., Grandi, G., Sun, L., Smith, H.O., Fraser, C.M., Moxon, E.R., Rappuoli, R. & Venter, J.C. (2000). Complete genome sequence of Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B strain MC58. Science. 287 (5459), 1809-1815.
Vandeputte-Rutten L., Bos M.P., Tommassen J. & Gros P. (2003). Crystal structure of Neisserial surface protein A (NspA), a conserved outer membrane protein with vaccine potential. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278(27), 24825-24830.
http://www.sanger.ac.uk/resources/downloads/bacteria/neisseria.html